May . 06, 2024 15:57 Back to list
A Comprehensive Guide to Deep Groove Ball Bearings
A Comprehensive Guide to Deep Groove Ball Bearings

Deep groove ball bearings are critical machinery components, silently enabling smooth and efficient motion in a myriad of applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the basics of deep groove ball bearings, exploring their functions, applications, construction, sealing types, materials, radial clearance options, and more.
Whether you are a seasoned engineer or a curious enthusiast, this article aims to demystify the world of deep groove ball bearings and highlight their crucial role in the realm of machinery.
What are Deep Groove Ball Bearings?
Deep groove ball bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing that facilitates the rotation of shafts and axles while minimizing friction.
They are known for their versatility and efficiency in handling both radial and axial loads. However, they are limited in terms of axial loads since they are mainly design as radial bearings. In other words, they can handle much higher radial loads compared to axial loads, thus meaning that they are preferred in high radial load applications.
The key design feature of deep groove ball bearings is their deep raceway grooves, which enable the bearings to accommodate a wide range of load types.
According to well-known manufacturer SKF, deep groove ball bearings can operate at high rotational speeds since they are optimized for low noise and low vibration.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Function
The primary function of deep groove ball bearings is to support radial and axial loads with certain limitations, and their main function is to reduce friction in rotating equipment.
The deep raceway grooves contribute to the bearings' ability to handle radial and axial loads in both directions, making them suitable for applications with bi-directional forces.
Additionally, deep groove ball bearings are designed for high-speed operation, but they can also operate at a wide variety of speeds, thus ensuring smooth and reliable performance in various settings.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Construction
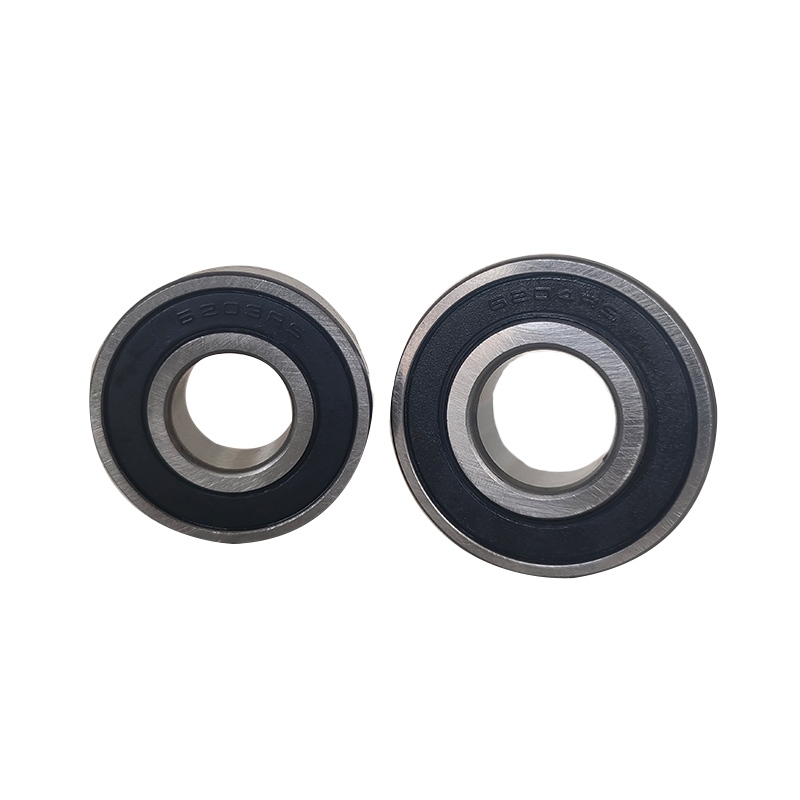
Deep groove ball bearings have a straightforward construction, consisting of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage that retains the balls in the raceway.
The inner and outer rings are typically made from high-quality steel, ensuring strength and durability. The cage material varies based on the application requirements and can be constructed from materials such as nylon, steel, or brass.
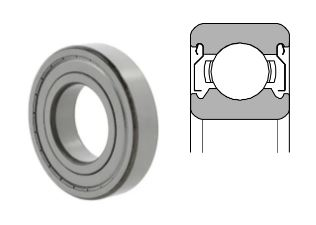
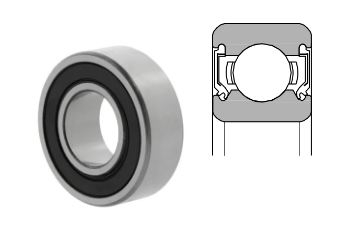
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Sealing Types
Deep groove ball bearings usually come in three forms: open, shielded, and sealed. The choice comes down to the requirements of the application, but more often than not, the sealed type is preferred to enhance their performance and longevity.
The shielded and sealed types are commonly known as maintenance-free bearings, a feature that makes them highly attractive for many applications.
Deep groove ball bearings often come equipped with various sealing options. Common sealing types include:
1. Metal Shields: Also known as non-contact sealing, these shields provide moderate protection against contaminants and are suitable for applications with lower contamination risk. Not suitable for water proofing.
A metal shield is attached to the outside ring. The inner ring incorporates a V-groove and labyrinth clearance to keep out dirt and seal in the grease.
2. Rubber Seals: Ideal for environments with high contamination levels, rubber seals provide enhanced protection against dust, moisture, and other external elements.
These seals are usually divided into two groups: non-contact, contact.
Non-contact rubber seals incorporate synthetic rubber molded to a steel plate in the outer ring. These seals are very good to keep dust and other contaminants out. However, they are not good for water proofing.
Contact rubber seals are very similar to non-contact rubber seals, but the edge of these ones is always in contact with the V-groove along the inner ring surface. These feature makes them the best choice for applications with a high exposure to contaminants since these seals can prevent any contaminant to enter into the grease, even water.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Materials
The choice of materials in deep groove ball bearings is crucial for their performance and longevity.
High-quality steel is the most common material for the inner and outer rings, while the balls can be made from steel, ceramic, or other advanced materials.
Ceramic balls, for instance, offer benefits such as reduced friction, increased rigidity, and resistance to corrosion.
As we mentioned in the previous point, we can find seals made of metal, but the most common sealing material is an environmentally friendly nitrile rubber compound.
20*47*14mm 6204-2RS C3 Deep Groove Ball Bearing
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Radial Clearance Options
Radial clearance, or the internal clearance between the rolling elements and the raceways, is a critical factor in deep groove ball bearings. It influences the bearings' thermal expansion and the ability to accommodate misalignment.
Common radial clearance options include:
1. CN (Normal Clearance): Suitable for standard operating conditions with moderate speeds and temperatures.
2. C3 (Greater than normal): Ideal for applications with higher temperatures or higher speeds, allowing for thermal expansion.
3. C4 (Greater than C3): Used in extreme conditions where high temperatures or very high speeds are encountered. It allows for thermal expansion too.
4. C0 (Tighter Clearance): Ideal for applications that require a reduced radial play.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Applications
Deep groove ball bearings find application in a diverse range of industries and machinery.
From automotive systems and electric motors to household appliances and industrial machinery, these bearings play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless motion.
Their widespread use is attributed to their efficiency, durability, and adaptability to different operating conditions.
Top applications include:
1. Automotive Industry: Wheel hubs, Gearboxes, Electric motors, Engine components
2. Electric Motors: AC and DC motors, Generators, Alternators,
3. Industrial Machinery: Conveyor systems, Fans and blowers, Pumps, Compressors
4. Household Appliances: Washing machines, Refrigerators, Air conditioners, Vacuum cleaners
5. Aerospace: Aircraft landing gear, Flight control systems
6. Mining Equipment: Conveyor belts, Crushers, Pulverizers
7. Power Tools: Drills, Grinders, Sanders
8. Medical Devices: Dental drills, Medical imaging equipment
9. Textile Machinery: Spinning machines, Weaving machines
10. Agricultural Machinery: Tractors, Harvesters, Seeders
11. Construction Equipment: Excavators, Bulldozers, Cranes
12. Material Handling Equipment: Forklifts, Conveyors, Lift trucks
13. Railway Applications: Locomotives, Railcar components
14. Oil and Gas Industry: Pumps, Compressors, Drilling equipment
15. Marine Industry: Propulsion systems, Winches, Pumps
16. Renewable Energy: Wind turbine generators, Solar tracking systems
17. Sports and Fitness Equipment: Exercise machines, Treadmills, Stationary bikes
18. Robotics: Robotic arms, Automated manufacturing systems
19. Instrumentation and Measurement Devices: Precision instruments, Measurement devices
20. Food and Beverage Industry: Conveyor systems, Packaging machinery
This list is by no means exhaustive, as deep groove ball bearings are integral to the functioning of countless mechanical systems across various industries. Their versatility, efficiency, and ability to handle diverse loads make them indispensable in the world of machinery and technology.
Latest news
-
Top Spherical Roller Bearing Material Exporter - High-Performance Alloys
NewsAug.27,2025
-
Durable PLC 110-190 Spherical Roller Bearing for Mixer Reducer
NewsAug.26,2025
-
CSK-2RS Sprag Clutch One Way Bearing: Sealed, High Torque, Durable
NewsAug.25,2025
-
CKZ-D Series One Way Overrunning Clutch: Reliable Power Control
NewsAug.24,2025
-
203KRR3 Round Bore Series Bearings | Cylindrical Outer Ring, Precision
NewsAug.23,2025
-
Top Spherical Roller Bearing Material Exporter - High Performance
NewsAug.22,2025